Find Doctors And Medical Facilities
Operational Technology (OT) cyber security is a complex and critical task, whether you are a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), OT Security Manager, or a security engineer responsible for defending critical OT assets, data, and infrastructure against advanced threats. Security frameworks can provide essential guidance.
Challenges in OT Cyber Security
Focus Areas: Identifying which aspects of cyber security to prioritize can be challenging. Balancing protection of assets, data, and infrastructure requires a strategic approach. Regulatory Compliance: Navigating an increasing number of regulations demands meticulous attention and resources. Ensuring compliance while managing day-to-day security operations can strain limited resources. Proactive Stance: Staying ahead of potential threats necessitates a proactive approach. Limited time and resources make it difficult to maintain continuous vigilance and responsiveness.
Role of Security Frameworks
Security frameworks act as a “compass,” guiding you through your OT cyber security and compliance journey. They offer structured and comprehensive approaches to managing and improving your security posture.
Benefits of Security Frameworks
Guidance and Direction: Frameworks provide a clear roadmap for addressing various aspects of cyber security. They help prioritize actions and resources effectively, ensuring critical areas are covered. Regulatory Alignment: Frameworks often align with industry regulations, aiding in compliance efforts. Using a recognized framework can simplify the process of meeting regulatory requirements.
Proactive Security Posture: Implementing a framework encourages a proactive stance on cyber security. Regular assessments and updates as per the framework help in anticipating and mitigating threats. Resource Optimization: Frameworks help maximize the impact of limited resources by focusing on high-risk areas. They facilitate efficient use of time and personnel, ensuring key security measures are implemented effectively.
Examples of Security Frameworks
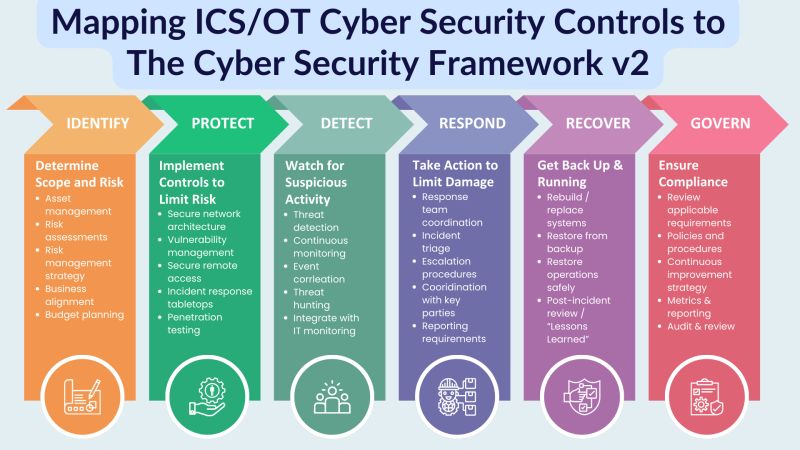
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF): Provides a comprehensive set of guidelines and best practices for managing cyber security risk. ISO/IEC 27001: Offers a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information, ensuring it remains secure.
CIS Controls: A set of recommended actions to protect and defend against cyber threats. ISA/IEC 62443: Specifically designed for industrial automation and control systems, addressing OT security needs.
Deploying an Operational Technology Cyber Security Framework (OT-CSF) eliminates the guesswork in securing OT assets. These frameworks provide cyber security managers with a reliable, standardized, and systematic approach to mitigating cyber risk, regardless of the OT environment’s complexity.
Why Deploy an OT Cyber Security Framework?
Benefits of an OT Cyber Security Framework
Strategic Planning: Offers a strategic and well-thought-out plan to protect OT assets, infrastructure, and data. Provides a structured approach to addressing cyber security challenges. Guidance and Adaptability: Offers guidance to security leaders, enabling intelligent management of cyber risks. Allows organizations to adapt and adjust existing well-known frameworks to meet specific needs, including compliance with commercial or government regulations.
Simplified Compliance: Helps organizations follow standard cyber security practices, making compliance easier and smarter. Ensures adherence to correct security procedures, providing tangible risk reduction.
Key Benefits of Deploying an OT Cyber Security Framework
- Time-Saving Structure: Provides a clear structure for taking action, saving time and effort. Helps map the current status of the OT cyber security journey and identify gaps, facilitating clear, actionable conversations with stakeholders.
- Facilitated Communication: Enhances communication with all stakeholders by clarifying requirements, roles, and responsibilities. Ensures everyone in the organization understands their role in cyber security.